The spermatoproteasome: a key enzymatic complex in spermatogenesis
The spermatoproteasome is found exclusively in mammalian germ cells and is essential for spermatogenesis. It differs from the constitutive proteasome by the presence of only one alternative protein out of the 14 constituting the complex. This work, published on April 4, 2022 in Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, shows that the few amino acids that distinguish the spermatoproteasome are sufficient to induce stronger structural dynamics and thus change its interactome and function.
The proteasome degrades non-functional proteins in order to avoid their aggregation, which could be deleterious, but also to regulate the concentration of certain key proteins inside cells. As such, the proteasome is at the center of many cellular signaling pathways. Its intracellular localization, still poorly described, also seems crucial to regulate the actors of various cellular processes, including replication, translation and differentiation.
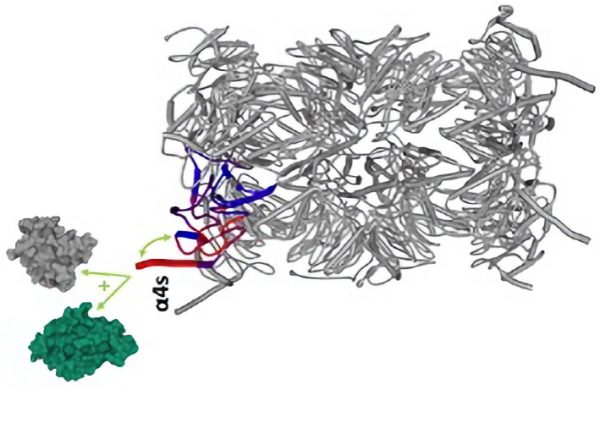
During evolution, the proteasome has diversified to fulfill different functions, depending on the cellular environment. Different types of proteasomes, containing alternative subunits, have emerged, such as the spermatoproteasome (s20S) in germ cells (ovaries and testes). The spermatoproteasome differs from the constitutive proteasome (c20S) by its non-catalytic α4s subunit which replaces the constitutive α4 subunit.
The crucial role of this α4s subunit in spermatogenesis has been demonstrated in mice: germ cells that do not express this protein block their differentiation. However, why the replacement of a single 20S proteasome subunit is essential for this process remains unclear. To better understand the structure-function relationships of the s20S during spermatogenesis, scientists analyzed mammalian germ cells at different states of differentiation with advanced mass spectrometry strategies. They observed an abrupt incorporation of α4s (>98%) during spermatogenesis and a very strong concomitant activation of s20S. In addition, s20S, unlike c20S, interacts with proteins of the synaptonemal complex, crucial for homologous recombination of chromosomes during meiosis. Finally, a structural approach led to the discovery that α4s is more dynamic in solution than α4, thus rationalizing the molecular bases of the functional specificity of this proteasome subtype.
These results could lead to a better understanding of the mechanisms of male infertility.
Proteasome complexes experience profound structural and functional rearrangements throughout mammalian spermatogenesis
Živković D, Sanchez Dafun A, Menneteau T, Schahl A, Lise S, Kervarrec C, Toste Rêgo A, da Fonseca PCA, Chavent M, Pineau C, Burlet-Schiltz O, Marcoux J, Bousquet MP
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA April 4, 2022 – DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2116826119